How were government methods to wage war during WWII similar? This intriguing question unveils striking parallels in the strategies employed by nations during the conflict. From economic mobilization to technological advancements and propaganda campaigns, governments exhibited remarkable similarities in their approaches to waging war.
The shared experiences of the Second World War fostered a convergence of wartime practices, reflecting the urgency and global scale of the conflict. Governments across the globe grappled with the challenges of mobilizing their economies, harnessing technological innovations, and rallying their populations behind the war effort.
Wartime Mobilization and Production
Governments across the globe implemented comprehensive mobilization plans to transform their economies into war-producing machines. These plans shared similarities in their approach, aiming to:
Centralize production
Governments established centralized control over industries, allocating resources and setting production targets.
Increase industrial capacity
Factories were expanded, new ones were built, and production lines were streamlined to maximize output.
Mobilize labor
Women, minorities, and other marginalized groups were recruited into the workforce to replace men who had gone to war.
Control raw materials
Governments secured access to essential resources, such as steel, oil, and rubber, through diplomacy or military action.Specific industries targeted for mobilization included aircraft production, shipbuilding, munitions manufacturing, and chemical industries.
Technological Advancements: How Were Government Methods To Wage War During Wwii Similar
Technological advancements played a pivotal role in shaping the conduct of WWII. Governments invested heavily in research and development, leading to:
Radar technology
Enabled the detection and tracking of enemy aircraft and ships, revolutionizing air and naval warfare.
Codebreaking
Allied codebreakers, such as the British at Bletchley Park, deciphered German and Japanese codes, providing crucial intelligence.
Nuclear weapons
The development of the atomic bomb by the United States ushered in a new era of warfare and raised questions about the future of humanity.Different governments utilized these technologies in varying ways, depending on their specific needs and capabilities.
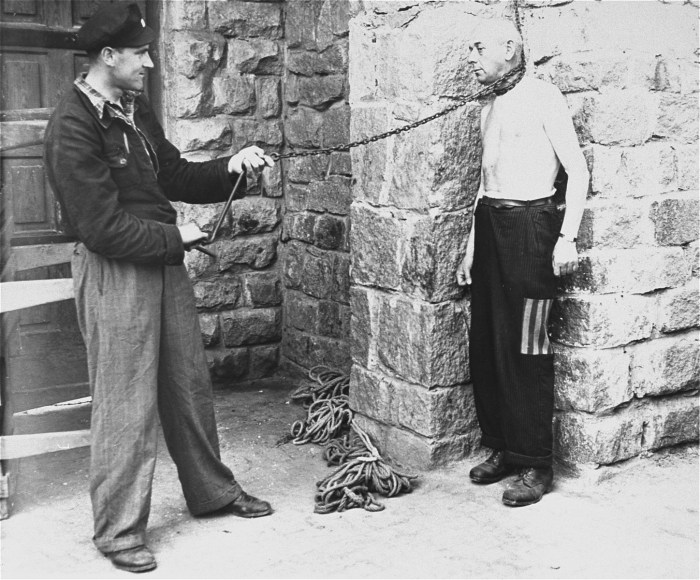
Intelligence Gathering and Espionage
Intelligence agencies played a vital role in WWII, providing governments with critical information about enemy plans and capabilities. Similarities in intelligence methods included:
Human intelligence
Agents were recruited and deployed to gather information through espionage, sabotage, and covert operations.
Signal intelligence
Interception and analysis of enemy communications provided valuable insights into their plans and movements.
Aerial reconnaissance
Reconnaissance aircraft flew over enemy territory to gather photographic and other intelligence.Successful intelligence operations included the breaking of the Enigma code by British codebreakers and the penetration of the German Abwehr by Allied agents.
Diplomatic Strategies

Diplomatic strategies were employed by governments to secure alliances, isolate enemies, and negotiate peace. Common goals included:
Building alliances
Alliances were formed to pool resources, coordinate military operations, and deter potential adversaries.
Isolating enemies
Governments sought to weaken enemy alliances and prevent them from gaining support from other countries.
Negotiating peace
Diplomatic efforts were made to end the war, often through mediation by neutral parties.Diplomatic alliances included the Axis powers (Germany, Italy, Japan) and the Allied powers (United States, Great Britain, Soviet Union).
Propaganda and Public Relations
Governments used propaganda to mobilize public support for the war effort. Techniques included:
Patriotic appeals
Propaganda emphasized the importance of defending the nation and its values.
Demonization of the enemy
Enemy nations were portrayed as evil or barbaric to rally public support.
Censorship and control of information
Governments restricted the flow of information to control public opinion and prevent dissent.Specific propaganda campaigns included the “Keep Calm and Carry On” posters in Britain and the “Uncle Sam” recruitment posters in the United States.
Civilian Involvement
Civilians played a significant role in the war effort, both on the home front and in occupied territories. Governments mobilized civilian resources through:
Wartime industries
Civilians worked in factories and other industries to produce war materials.
Civil defense
Civilian organizations provided air raid protection, fire-fighting services, and other essential services.
Resistance movements
In occupied territories, civilians organized resistance movements to sabotage enemy operations and provide intelligence to Allied forces.Civilian organizations included the Home Guard in Britain, the Volunteer Air Observer Corps in the United States, and the French Resistance in occupied France.
Answers to Common Questions
What were the key technological advancements used in WWII?
Governments invested heavily in developing and deploying new technologies, including radar, sonar, jet aircraft, and atomic weapons, which had a profound impact on the conduct of war.
How did governments mobilize their economies for war production?
Governments implemented comprehensive economic measures, such as rationing, price controls, and the conversion of civilian industries to war production, to maximize their output of essential war materials.
What role did propaganda play in mobilizing public support for the war effort?
Governments employed a range of propaganda techniques, including posters, films, and radio broadcasts, to shape public opinion, boost morale, and demonize the enemy.