Long term potentiation ap psych example – Long-term potentiation (LTP) emerges as a pivotal phenomenon in the realm of neuroscience, shedding light on the intricate mechanisms underlying memory formation and cognitive function. This article delves into the captivating world of LTP, exploring its fundamental principles, experimental paradigms, and far-reaching implications for understanding brain development and plasticity.
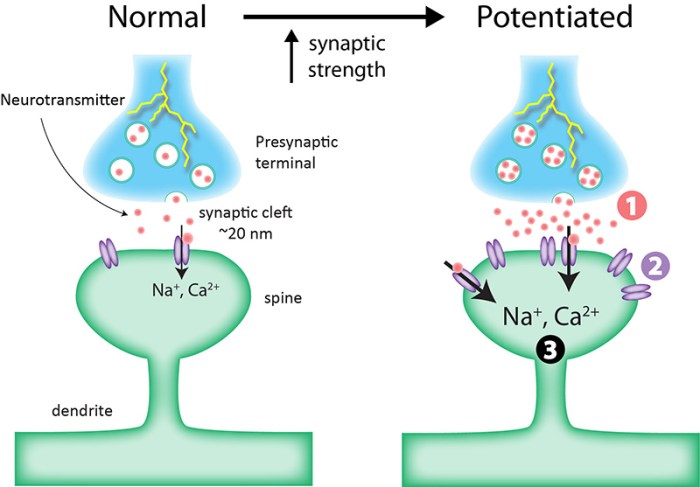
LTP, a persistent enhancement in synaptic strength, serves as a cornerstone in the formation of long-lasting memories. Its discovery has revolutionized our comprehension of how the brain encodes and retrieves information, opening new avenues for research into learning and memory disorders.
Introduction to Long-Term Potentiation (LTP)
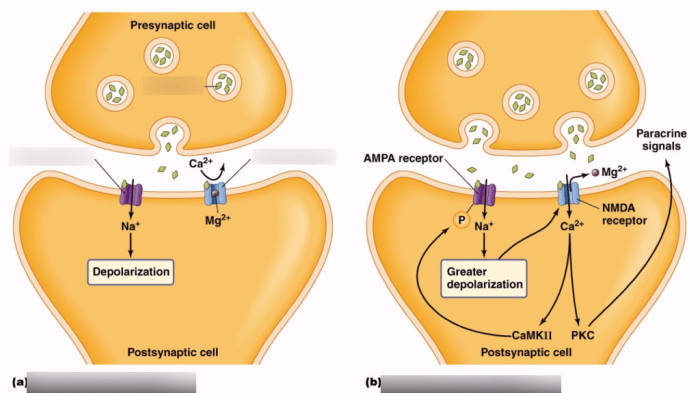
Long-term potentiation (LTP) is a persistent increase in synaptic strength that occurs following high-frequency stimulation of a synapse. LTP is believed to be a cellular mechanism underlying memory formation and storage.
The basic mechanisms underlying LTP involve the activation of NMDA receptors, which leads to an influx of calcium ions into the postsynaptic neuron. This calcium influx triggers a cascade of intracellular signaling events that ultimately lead to the strengthening of the synapse.
LTP is a highly significant process in learning and memory. It is thought to be responsible for the long-term storage of information in the brain.
Experimental Paradigms for Studying LTP

Electrophysiological Techniques
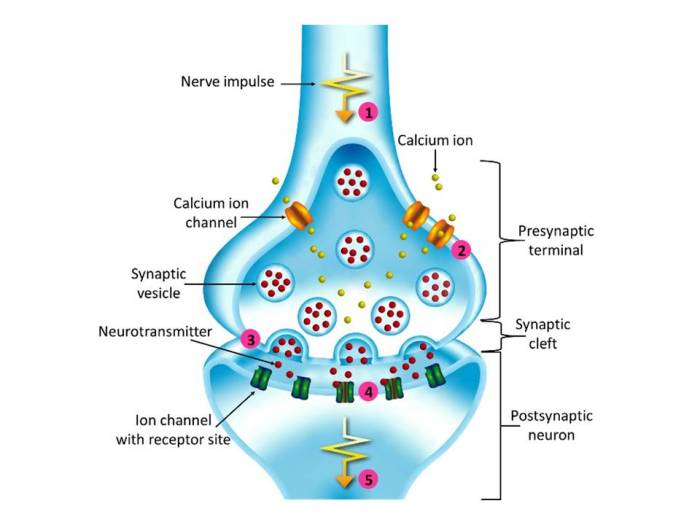
LTP is typically induced and measured using electrophysiological techniques. These techniques involve recording the electrical activity of neurons in response to synaptic stimulation.
Types of LTP Protocols, Long term potentiation ap psych example
There are several different types of LTP protocols that can be used to induce LTP. The most common protocol is high-frequency stimulation, which involves delivering a train of high-frequency electrical pulses to the synapse.
Another common protocol is theta-burst stimulation, which involves delivering a series of bursts of electrical pulses at a theta frequency (4-8 Hz).
Importance of Experimental Controls
It is important to use appropriate experimental controls when studying LTP. These controls help to ensure that the observed effects are due to LTP and not to other factors, such as changes in neuronal excitability.
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of LTP
Role of NMDA Receptors
NMDA receptors play a critical role in the induction of LTP. These receptors are activated by glutamate, which is released from the presynaptic neuron during synaptic transmission.
When NMDA receptors are activated, they allow calcium ions to enter the postsynaptic neuron. This calcium influx triggers a cascade of intracellular signaling events that ultimately lead to the strengthening of the synapse.
Intracellular Signaling Pathways
The intracellular signaling pathways involved in LTP include the activation of protein kinases and gene expression.
Protein kinases are enzymes that phosphorylate other proteins, thereby altering their activity. Gene expression refers to the process by which genes are transcribed into mRNA and then translated into proteins.
Structural Changes
LTP is associated with a number of structural changes at the synapse. These changes include the addition of new AMPA receptors to the postsynaptic membrane and the enlargement of dendritic spines.
LTP in Different Brain Regions
Hippocampus
LTP is particularly well-studied in the hippocampus, which is a brain region that is involved in memory formation.
In the hippocampus, LTP is thought to be responsible for the storage of long-term memories.
Cortex
LTP also occurs in the cortex, which is a brain region that is involved in a variety of cognitive functions, including perception, attention, and decision-making.
In the cortex, LTP is thought to be responsible for the storage of working memories.
Amygdala
LTP also occurs in the amygdala, which is a brain region that is involved in emotional processing.
In the amygdala, LTP is thought to be responsible for the storage of emotional memories.
Applications of LTP Research: Long Term Potentiation Ap Psych Example
Therapeutic Applications
LTP research has potential therapeutic applications for the treatment of memory disorders and neurodegenerative diseases.
For example, LTP-enhancing drugs could be used to improve memory in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
Research Tool
LTP can also be used as a tool for studying learning and memory disorders.
For example, researchers can use LTP to study the effects of different drugs or treatments on memory.
Educational Practices
LTP research can also inform educational practices and enhance learning outcomes.
For example, teachers can use LTP to design learning activities that are more likely to promote long-term retention.
User Queries
What is the significance of LTP in memory formation?
LTP is a fundamental mechanism underlying the formation of long-term memories. It strengthens synaptic connections between neurons, allowing for the storage and retrieval of information over extended periods.
How is LTP induced experimentally?
LTP can be induced in the laboratory using various electrophysiological techniques, such as high-frequency stimulation or theta-burst stimulation, which mimic the patterns of neuronal activity that occur during learning.
What are the molecular mechanisms involved in LTP?
LTP involves a cascade of molecular events, including the activation of NMDA receptors, the influx of calcium ions, and the activation of protein kinases and gene expression, leading to structural changes at the synapse.